Universe is Vibration
( Work in progress )
Vibration
"Everything is energy. Match the frequency of the reality you want and you cannot help but get that reality. It can be no other way. This is not philosophy. This is physics."
All matter in our universe are in constant motion - vibrating or spinning. Even objects that appear to be stationary are in fact vibrating, oscillating, resonating at various frequencies. All organisms are made out of atoms and molecules, which means literally every living thing is radiating energy and vibration. Every living thing on earth vibrates at its own level with its own sound, determined by the velocity of its frequency. Motion generates frequencies and in turn, generates sound whether we are able to hear it or not. Everything has a sound, and it's own level of vibration. The specific sound is determined by the velocity (frequency) of the movement. All organisms on this planet use vibration that is, energy, as the primary means of communication. In its original condition vibration is inaudible and invisible, but in its first stage towards manifestation it becomes audible, and its next step is visible.
In 1905, scientists discovered that all matter is a form of energy. They concluded energy cannot be created or destroyed, but only converted from one form to another. Matter can be considered a form of energy too and can be converted into energy. Furthermore, energy can also be converted into matter.
"If you want to find the secrets of the universe, think in terms of energy, frequency and vibration."
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon, a periodic back-and-forth motion of the particles of an elastic body or medium, commonly resulting when almost any physical system is displaced from its equilibrium condition and allowed to respond to the forces that tend to restore equilibrium, or in more simple terms, phenomenon, whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. From French vibration, from Latin vibrātiō ("a shaking or brandishing"), from vibrō ("shake, vibrate"). Vibrate comes from Latin vibrātus, perfect passive participle of vibrō ("agitate, set in tremulous motion"), ultimately from Proto-Indo-European *weyp- ("to oscillate, swing") or *weyb-.
Frequency: A Simple Explanation
Frequency is a way to describe how often something happens within a certain amount of time. In science, especially in physics and chemistry, the word "frequency" is usually used when talking about waves. These waves can be light waves, sound waves, or radio waves.
For example, when a wave moves, we can look at one point on the wave and count how many times that point passes by a specific spot in one second. The number of times it passes is called the frequency. The unit for frequency is usually hertz (Hz), where 1 hertz means one wave cycle per second.
Where Does the Word Come From?
The word frequency comes from the Latin word frequentia, which means "a crowd" or "a repeated occurrence". This Latin word comes from frequens, meaning "crowded" or "often occurring".
Digging deeper, frequens may have come from the Proto-Italic word frekʷents, and possibly from the older Proto-Indo-European root bʰrekʷ-, which means "to stuff". This makes sense, because something that happens frequently can feel like it’s being "stuffed" into a short period of time.
Some related words and ideas come from Latin and Ancient Greek. For instance, Latin farciō means "to cram or stuff", and Ancient Greek φράσσω (phrássō) means "to block or fence in". There may also be a connection to the Proto-Indo-European word bʰerǵʰ-, meaning "high," which is linked to the English word berg (as in iceberg).
Why is Frequency Important?
Frequency helps us understand how waves behave. For example, in sound, a higher frequency means a higher pitch, like the sound of a whistle. In light, a higher frequency means the light appears bluer, while a lower frequency gives a redder color. In radio, different frequencies allow different stations to broadcast without interfering with each other.
In short, frequency is a simple yet powerful idea that helps us make sense of many things in the world around us, from music and color to technology and nature.
Further reading and references:
- What is frequency? - QRG
- Frequency - Wikipedia
- What is Frequency? - YouTube
- What is Frequency ? Frequency Explained. What is Hz? - YouTube
- What is Frequency? - ECS Inc. International
- What Is Frequency? - Definition, Spectrum & Theory - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
- Physics Tutorial: Frequency and Period of a Wave
- Glossary: Frequency
Resonance: A Simple Guide
Resonance is a natural effect that happens when a vibrating object or force makes another object start to vibrate with more energy. This happens when both objects share the same natural frequency. In simple words, resonance occurs when something is vibrating and causes another object nearby to vibrate too - but with a stronger movement.
What is Resonant Frequency?
Every object has its own natural frequency, which is the speed or rate at which it likes to vibrate. When another force or wave with the same frequency hits that object, it begins to vibrate more strongly. This matching point is called the resonant frequency. When an object is hit with its resonant frequency, it can vibrate so much that it may even break or become unstable.
A Common Example: A Swing
A good example of resonance is pushing someone on a swing. If you push the swing at just the right time - matching the swing’s natural rhythm - it goes higher and higher with very little effort. That timing is the swing’s resonant frequency. If you try to push too fast or too slow, it doesn’t work as well.
Everyday Examples of Resonance
Resonance happens in many parts of daily life and in nature:
Playing a Guitar: When you pluck a string, it vibrates and causes the air around it to vibrate too. If another string has a similar natural frequency, it may start to vibrate on its own - this is resonance.
Breaking a Wine Glass with Voice: A trained singer can hit a note that matches the natural frequency of a wine glass. When the sound wave matches the resonant frequency of the glass, the glass can vibrate so much that it shatters.
Tacoma Narrows Bridge Collapse: In 1940, strong winds caused the Tacoma Narrows Bridge in the United States to sway and eventually break apart. The wind matched the bridge’s natural frequency, creating resonance and causing it to vibrate wildly.
Pushing a Pendulum: Like the swing, a pendulum (a hanging weight that swings back and forth) will move higher if pushed in rhythm with its natural swinging speed.
Why is Resonance Important?
Resonance can be useful or dangerous. In music, it helps produce rich sounds. In engineering, it must be carefully managed because too much vibration can damage buildings, bridges, and machines. That’s why understanding resonance is important in designing safe structures and useful tools.
In short, resonance is a powerful effect that happens when vibrations match. It helps us create music, understand sound, and design better structures - but it can also lead to unexpected problems if not carefully controlled.
Energy
"Everything is energy. Match the frequency of the reality you want and you cannot help but get that reality. It can be no other way. This is not philosophy. This is physics."
In science, especially in physics, energy is the ability to do work or cause change. It is what makes things move, heat up, light up, or grow. Without energy, nothing would happen - machines wouldn’t run, plants wouldn’t grow, and we wouldn’t be able to move.
Different Types of Energy
Energy comes in many different forms, and each one plays an important role in our everyday lives:
Kinetic Energy: This is the energy of motion. A moving car, a falling ball, or even a running person all have kinetic energy.
Potential Energy: This is stored energy. For example, a rock sitting at the edge of a cliff has potential energy because of its position. If it falls, that energy turns into kinetic energy.
Thermal Energy: Also called heat energy, it comes from the movement of tiny particles inside matter. The faster these particles move, the hotter the object becomes.
Electrical Energy: This is the energy that comes from the movement of electric charges. It powers things like lights, computers, and appliances.
Chemical Energy: Stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules, this energy is released in chemical reactions - like when we digest food or when fuel burns.
Nuclear Energy: This energy is stored in the nucleus of atoms. It can be released through nuclear reactions, such as in the sun or nuclear power plants.
Energy and Motion
All forms of energy are connected to motion in some way. Even when something seems still, like a rock or a battery, it holds energy that can lead to motion or action under the right conditions.The Law of Conservation of Energy
One of the most important rules in science is that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be changed from one form to another. This idea is known as the conservation of energy, or the first law of thermodynamics. For example, when you eat food (chemical energy), your body uses it to move (kinetic energy) and stay warm (thermal energy).The Sun: Our Main Energy Source
For most life on Earth, the Sun is the main source of energy. Plants use sunlight to make food through photosynthesis. Animals eat plants, or other animals that eat plants, and gain energy. The sun also drives the weather, powers the water cycle, and helps keep our planet warm enough to live on.Why Is Energy Important?
Energy is essential for everything we do. From turning on a light to driving a car, to growing food and powering cities, we rely on energy every moment of the day. Learning about energy helps us understand the world and how to use resources wisely.
In short, energy is what powers the universe - and understanding it helps us live better and more sustainably.
Further reading and references:
- Energy - Wikipedia
- World's Most Asked Questions: What Is Energy? - YouTube
- What the HECK is Energy? - YouTube
- What Is Energy? A Deep Dive Into Understanding Energy
- What is energy? - Cosmos magazine
- What Is Energy? A Guide to Understanding Energy
- What is energy? - QRG
- What is energy? explained - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)
- Forms of energy - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)
- Sources of energy - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)
- Laws of energy - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)
- What is Energy? on Vimeo
Sound
"If a tree falls in a forest and no one is around to hear it, does it make a sound?"
Sound is a type of energy that we can hear. It is made by vibrations - small, rapid movements back and forth. When something vibrates, it creates waves of pressure that move through the air, water, or another material. These waves carry energy from one place to another, and when they reach our ears, we hear them as sound.
How Is Sound Made?
Sound starts with a vibrating object. For example, when you pluck a guitar string, it begins to vibrate. These vibrations push and pull the air around them. The moving string makes the air particles nearby move too. Those particles then bump into other particles, causing them to move. This chain reaction creates a pressure wave that travels through the air - this is the sound wave.
This process can happen in any medium - air, water, or even solid materials. However, sound cannot travel through a vacuum (like outer space) because there are no particles to carry the vibration.
How Does Sound Travel?
Sound travels in waves. These waves are called longitudinal waves, which means the particles in the medium move back and forth in the same direction that the wave is going. As the particles move, they create areas where they are close together (called compressions) and areas where they are spread apart (called rarefactions). These patterns move outward from the sound source like ripples in a pond.
How Do We Hear Sound?
When sound waves reach our ears, they make our eardrums vibrate. These vibrations are passed through tiny bones in the middle ear and then changed into signals that our brain understands as sound. This allows us to hear music, speech, noise, and all the other sounds around us.
Examples of Sound in Daily Life
Speaking and Singing: Your vocal cords vibrate to create sound when you talk or sing.
Musical Instruments: A drum, guitar, or flute produces sound when part of the instrument vibrates.
Animals: Birds chirping, dogs barking, and dolphins clicking all use sound to communicate.
Nature: Thunder, wind rustling leaves, and waves crashing on the beach are all natural sounds caused by movement and vibration.
Why Is Sound Important?
Sound helps us communicate, enjoy music, stay safe (like hearing a car horn), and understand our environment. It also plays a key role in technology, such as in phones, alarms, and medical devices like ultrasound.
In short, sound is energy we can hear, created by vibrations that travel through the air or other materials. It connects us to the world and to each other in many important ways.
Further reading and references:
Light
Light is a type of energy that allows us to see the world around us. Without light, our eyes would not be able to detect anything - everything would be completely dark. Light helps us see colors, shapes, and movement, and it plays a big role in our daily lives.
The Scientific Definition of Light
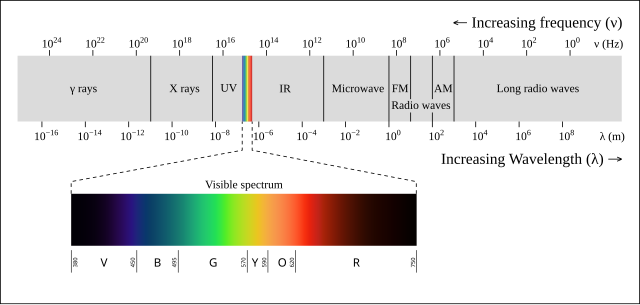
In science, light is defined as a type of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. This means it is part of a larger group of energy waves that also includes radio waves, microwaves, X-rays, and more. Light waves travel through space and do not need air or any other substance to move. That’s why light from the Sun can travel all the way through space to Earth.
Light Makes Things Visible
Light is the natural energy that stimulates sight - in simple terms, it is what allows us to see. When light shines on an object, some of it reflects off the object and enters our eyes. Our eyes then send signals to the brain, which helps us understand what we are seeing. That’s how we can see people, animals, buildings, books, and everything else around us.
Sources of Light
There are two main types of light sources:
Natural Sources: The Sun is the main natural source of light for Earth. It gives us daylight and provides energy for plants to grow. Other natural sources include stars and lightning.
Artificial Sources: These are man-made lights such as light bulbs, lamps, flashlights, and streetlights. These lights help us see when it is dark.
How Light Travels
Light travels in straight lines and moves very fast - almost 300,000 kilometers per second (about 186,000 miles per second) in a vacuum. When light hits a surface, it can do several things:
- Reflect (bounce off, like in a mirror)
- Refract (bend, like when light passes through water or glass)
- Absorb (soak into the material, turning into heat)
Why Is Light Important?
Light is essential for life. It helps plants grow through a process called photosynthesis, which also produces the oxygen we breathe. It helps animals and people see, find food, and stay safe. Light also affects our mood, health, and even our sleep patterns.
In modern life, we also use light in many technologies - in screens, cameras, lasers, fiber optics, and medical tools.
Conclusion
Light is a powerful and important form of energy that allows us to see and supports life on Earth. It comes from both natural and man-made sources, travels quickly, and helps us connect with and understand the world around us.
Further reading and references:
Break a White light
When a beam of white light passes through a triangular glass prism, something interesting happens - the light spreads out into a rainbow of colors. This process is called dispersion. The prism bends the light, and because each color in the white light has a different wavelength, each one bends a little differently.
- Red light has a longer wavelength, so it bends less.
- Blue and violet light have shorter wavelengths, so they bend more.
As a result, the white light is separated into a spectrum of colors - red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. This is the same effect we see in a rainbow, where sunlight passes through tiny water droplets in the air and gets split into colors.
What Is White Light?
White light is a combination of all the colors of the visible spectrum. It may look colorless to our eyes, but it is actually made up of many different wavelengths of light blended together.
The Sun is the main natural source of white light. Stars also give off white light, though some may appear to be different colors depending on their temperature and distance from Earth.
How the Sun Helps Life on Earth
Sunlight is not just important for seeing - it is also the main source of energy for life on Earth. The energy from sunlight powers a process in green plants called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants take in sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide and turn them into sugars, usually stored as starch. These sugars give plants the energy they need to grow.
When animals and people eat these plants, they also get energy. In this way, almost all living things get their energy from the Sun, either directly (like plants) or indirectly (like animals and humans who eat plants or other animals).
Other Sources of Light
Besides the Sun and stars, fire has been an important source of light for humans throughout history. Long before electric lights were invented, people used fire - such as torches, candles, and oil lamps - to light their homes and surroundings at night.
Today, we also use artificial light sources, like light bulbs and LEDs, but the basic idea remains the same: light helps us see, live, and survive.
Conclusion
When white light passes through a prism, it breaks apart into a rainbow of colors because each color bends differently. The Sun, our main source of white light, not only helps us see but also provides energy to plants and, through them, to nearly all living things. Understanding light helps us see the connection between science, nature, and life itself.
Further reading and references:
Color
Color is what we see when light reflects off an object and reaches our eyes. It is not something the object has by itself, but rather how our eyes and brain respond to the light it reflects or gives off. The way an object interacts with light - by absorbing some parts of it and reflecting others - determines what color we see.
You Need Light to See Color
Color cannot be seen without light. When light shines on an object, some parts of the light (called wavelengths) are reflected, and others are absorbed. The color that bounces off and reaches our eyes is the one we see. For example:
- If an object reflects only red light, we see it as red.
- If it reflects all colors of light equally, we see it as white.
- If it absorbs all colors and reflects none, we see it as black.
Why Do We See White or Black?
When white light - such as sunlight - hits a white object, none of the colors in the light are absorbed. Instead, they are all reflected equally, so the object looks white.
On the other hand, a black object absorbs all the colors in the light and reflects none back to our eyes, which is why it looks black.
What Is White Light?
The light from the Sun is called white light. It is actually made up of all the colors of the visible spectrum mixed together. You can see these colors when sunlight passes through a prism or appears in a rainbow - red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Different Colors, Different Wavelengths
Each color of light has a different wavelength, which is the distance between two wave peaks in the light wave:
- Red light has the longest wavelength that our eyes can see.
- Violet light has the shortest wavelength.
The color of an object depends on which wavelengths it reflects and which it absorbs. Our eyes are able to detect these different wavelengths and send signals to the brain, which then tells us what color we are seeing.
Why Is Color Important?
Color helps us understand the world. It lets us tell objects apart, enjoy art and nature, and communicate emotions. Colors are also used in signs, clothing, traffic lights, and much more to send messages and create meaning.
Conclusion
Color is the result of how an object reflects or absorbs light. We see different colors depending on which parts of the light spectrum bounce off an object and reach our eyes. Without light, we wouldn’t see any color at all. Light, color, and vision all work together to help us make sense of the world.
Rainbow
A rainbow is a beautiful, curved band of many colors that appears in the sky, often after it rains. It happens when light from the Sun shines through water droplets in the air. These droplets act like tiny prisms, bending and splitting the light into a spectrum of colors. This is why we see a rainbow made up of several different colors in a specific order.
The most common time we see a rainbow is after a rainstorm, when sunlight shines through the raindrops. But rainbows can also appear in other places, such as near waterfalls, sea spray, or even fountains, wherever tiny water droplets are floating in the air and sunlight is shining through them.
How Does a Rainbow Form?
A rainbow forms because of two main things that happen to light when it enters water droplets:
- Refraction: This is when light bends as it passes from one material to another, such as from air into water.
- Reflection: This is when light bounces off the inside of the water droplet.
As sunlight enters a raindrop, it bends (refraction), then reflects off the back of the drop, and finally bends again as it leaves the drop. This process separates the light into its different colors, just like a glass prism does.
Why Is a Rainbow an Optical Illusion?
A rainbow is actually an optical illusion, meaning it’s not a real object you can touch or approach. The colors you see in a rainbow depend on where you are standing and where the Sun is behind you. No two people see exactly the same rainbow because it changes with your position. If you move, the angle between the Sun, the raindrops, and your eyes changes, and so does the rainbow.
Colors of the Rainbow
A rainbow always shows its colors in the same order - from the longest wavelength to the shortest. These are the seven main colors in a rainbow:
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Indigo
- Violet
These colors are sometimes remembered by the name ROYGBIV, using the first letter of each color. Red is on the outside of the rainbow and has the longest wavelength, while violet is on the inside with the shortest wavelength.
Conclusion
A rainbow is a colorful arc in the sky that happens when sunlight shines through water droplets and gets bent and reflected. This process separates the light into different colors that we see in a specific order. While it may look like a physical object, a rainbow is really an optical illusion that depends on the angle between the Sun, water, and the person seeing it. Rainbows are one of nature’s most beautiful displays and remind us of the amazing way light works.
Spiritual Vibration
Spiritual vibration is the idea that everything in the universe, including human thoughts and emotions, has a certain frequency or energy level. Just like sound and light travel in waves, many spiritual traditions believe that our consciousness - our thoughts, feelings, and awareness - also emits energy in the form of vibrations.
In this view, a person's inner state can affect not only their own life but the world around them. The higher the vibration, the more positive and connected we feel. Lower vibrations are linked to fear, sadness, or anger.
Reality as a Field of Vibration
According to both ancient wisdom and modern science, everything is made of energy. Quantum physics shows that even solid matter is actually made up of vibrating particles. This leads many to suggest that our reality is more like a sea of energy - a vibrating field that responds to awareness, intention, and emotion.
- When people speak about "raising your vibration," they mean becoming more aware, positive, and aligned with love, peace, and clarity.
- Lower vibrations are associated with stress, fear, and disconnection from yourself and others.
This idea is echoed in traditions like Hinduism, Buddhism, and mystical Christianity, as well as in New Age and energy healing practices.
How Human Awareness Affects Reality
Your thoughts, emotions, and beliefs have power. When many people focus on something together, it can influence outcomes. This is sometimes called collective consciousness.
Here are some examples of how human vibration may influence reality:
Emotional Fields: Studies by the HeartMath Institute suggest that our hearts create measurable electromagnetic fields that affect people around us. Calm, loving states create a more coherent heart rhythm, which is linked to better health and emotional balance.
Water and Emotion: Dr. Masaru Emoto conducted experiments showing that water crystals form beautiful shapes when exposed to positive words or music and ugly shapes when exposed to negativity. While controversial, his work is widely known in spiritual circles.
The Placebo Effect: Scientifically, the placebo effect shows how belief can trigger healing - just expecting a benefit causes real changes in the body.
Meditation Studies: Group meditations have been shown to reduce crime rates and violence in certain areas during the practice, according to several studies, including the Maharishi Effect.
Signs of High and Low Vibrations
| High Vibration | Low Vibration |
|---|---|
| Joy, peace, gratitude | Anger, fear, jealousy |
| Love and compassion | Hate, blame, victimhood |
| Inspiration and creativity | Hopelessness, disconnection |
| Flow, synchronicity | Conflict, struggle, resistance |
How to Raise Your Vibration
Raising your vibration means becoming more aware of your inner state and making intentional choices that support harmony and growth. Here are simple ways to do that:
- Meditation and mindfulness
- Spending time in nature
- Practicing gratitude
- Eating healthy, whole foods
- Letting go of negative thoughts
- Listening to uplifting music or chanting
- Connecting with loving people
- Being of service to others
- Taking care of your body and sleep
Spiritual Vibration and Astrology
Astrology also works on the principle that planetary movements influence our energy patterns. Each planet, sign, and transit carries its own "vibration," and a person’s birth chart shows their unique energetic blueprint.
Just like sound and light frequencies, these cosmic energies interact with your personal vibration, influencing your mood, health, relationships, and spiritual growth. As your vibration rises, your awareness of these patterns also grows, allowing you to live with more purpose and alignment.
Conclusion
"You Are a Vibrational Being"
Everything in the universe is vibration - from the stars and planets to your own body and mind. Your thoughts, emotions, and level of awareness all contribute to the energy you emit and the reality you experience. By becoming more conscious and raising your spiritual vibration, you can influence not only your life but the world around you.
Whether seen through the lens of science, spirituality, or astrology, the message is the same: you are powerful, connected, and vibrational. The more aware you become of your inner state, the more you can shape your outer world.
Conclusion
All the topics we've explored - frequency, resonance, energy, sound, light, color, and rainbows - are closely connected through the science of waves and vibration. These natural forces show us how energy moves through the world and shapes everything we see, hear, and feel. From the sound of music to the colors we see in a rainbow, vibration and light are at the heart of how we experience reality.
Although astrology is not a traditional science like physics or chemistry, it is deeply inspired by the same universal forces - the rhythms of light, motion, and energy. Astrology reflects how these patterns influence human life, offering a symbolic way to understand our emotions, behaviors, and spiritual growth.
In this way, astrology bridges the gap between the physical and the spiritual, using the language of vibration and cosmic energy to explore the deeper meaning behind our experiences. Whether through science or symbolism, these universal energies connect us all to the greater flow of life.